The Court System- Georgia's Judicial Branch
SS8CG4- Analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
A. Describe the ways that judges are selected in Georgia.
B. Analyze the dual purpose of the judicial branch: to interpret the laws of Georgia and administer justice in our legal system.
C. Explain the difference between criminal law and civil law.
D. Explain the steps in the adult criminal justice system beginning with arrest.
A. Describe the ways that judges are selected in Georgia.
B. Analyze the dual purpose of the judicial branch: to interpret the laws of Georgia and administer justice in our legal system.
C. Explain the difference between criminal law and civil law.
D. Explain the steps in the adult criminal justice system beginning with arrest.
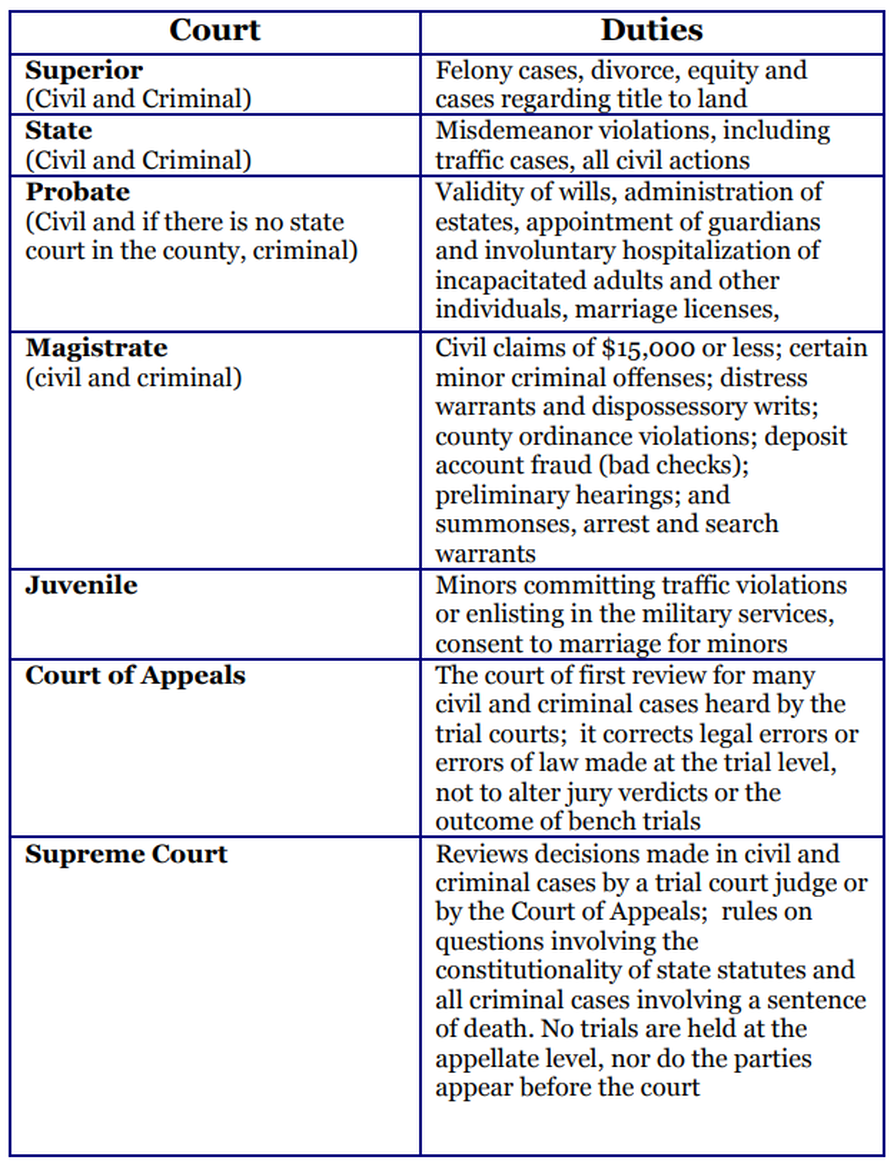
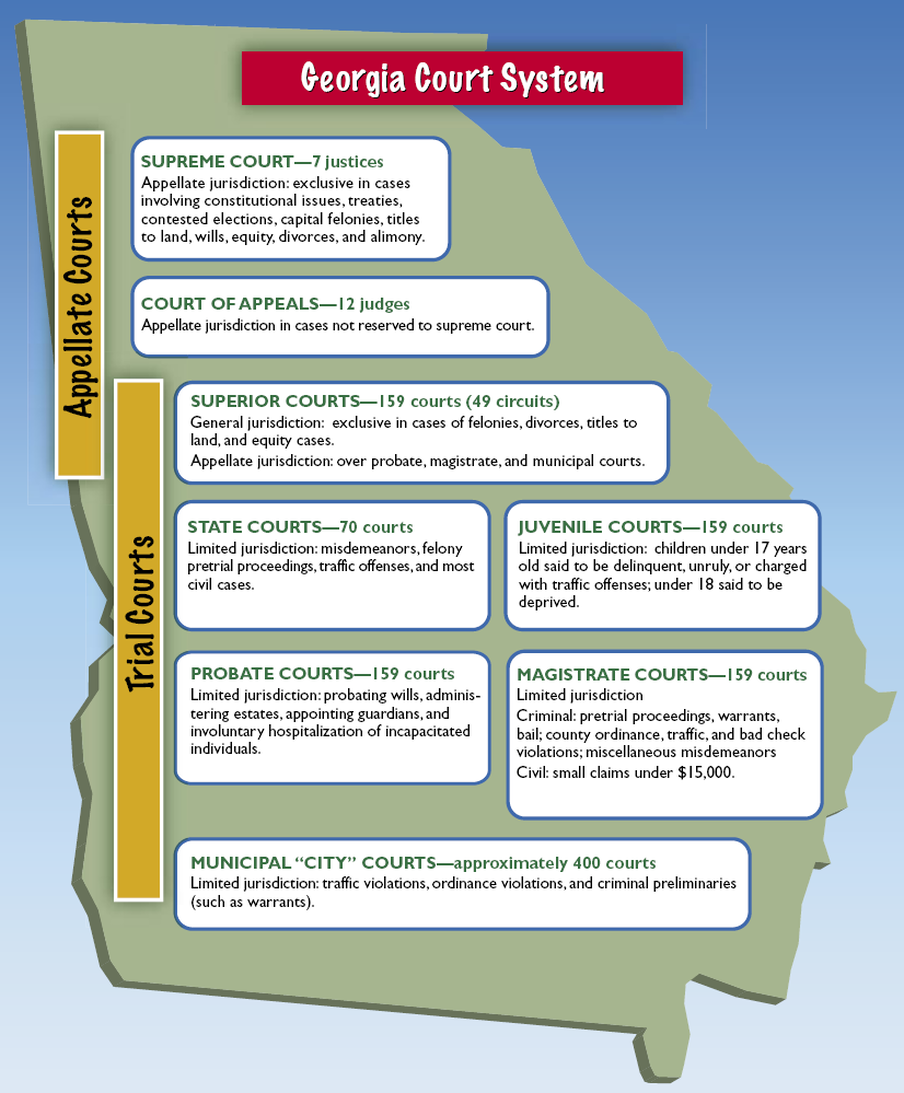
Trial and Appellate Courts
Georgia’s Courts fall in one of two categories — trial or appellate.
Trial courts have original jurisdiction; they are the first court to hear a case. There are five types of trial courts: State, Juvenile, Probate, Magistrate courts and the most common trial court is the Superior Court.
Each county in Georgia is required to have a Superior Court and will hear any civil or criminal case.
Appellate courts review cases that have already been decided by a lower court. The Court of Appeals of Georgia and the Supreme Court of Georgia each have specific cases they will hear, reexamining past decisions.
Trial courts have original jurisdiction; they are the first court to hear a case. There are five types of trial courts: State, Juvenile, Probate, Magistrate courts and the most common trial court is the Superior Court.
Each county in Georgia is required to have a Superior Court and will hear any civil or criminal case.
Appellate courts review cases that have already been decided by a lower court. The Court of Appeals of Georgia and the Supreme Court of Georgia each have specific cases they will hear, reexamining past decisions.
Terms of Office
Judges for all courts, except the juvenile courts, are elected in non-partisan elections. Judges in courts with original jurisdiction are elected for four year terms; appellate court judges are elected to six year terms. However, the Governor has the power to fill vacancies between elections.
Criminal and Civil Cases/ Felonies and Misdemeanors
The courts protect citizens from each other by handling civil cases (disputes between two or more persons or groups) and criminal cases (cases involving violations of the law).
Crimes are divided into felonies and misdemeanors.
*A felony is a serious crime such as murder or burglary, punishable by a year or more in prison, a fine of at least $1,000, or both.
**A misdemeanor is a less serious crime punishable by less than a year in prison, a fine of less than $1,000, or both.
Crimes are divided into felonies and misdemeanors.
*A felony is a serious crime such as murder or burglary, punishable by a year or more in prison, a fine of at least $1,000, or both.
**A misdemeanor is a less serious crime punishable by less than a year in prison, a fine of less than $1,000, or both.
Steps in Adult Criminal Justice System
1. When an adult suspect is placed under arrest, he or she is taken into custody.
2. Authorities place the suspect in a holding cell and make an official record of the arrest-booking.
3. The suspect makes an initial appearance before a magistrate judge who explains the charges makes sure that the suspect is given due process.
4. Next is the preliminary hearing to determine if there is probable cause that the suspect committed the crime.
5. If the case is sent to a grand jury they determine whether an indictment (a formal accusation of a serious crime) will be made.
6. If indicted, the suspect has an arraignment before a superior court. The judge allows the suspect to enter a plea.
7. If a suspect pleads not guilty, a court date is set and a trial is conducted unless a plea bargain is made (suspect admits guilt immediately for a shorter sentence).
8. Trials begin with jury selection.
9. Once the jury is selected, prosecution and defense attorneys present opening statements to the jury.
10 Both sides present evidence and cross-examine witnesses
11. Closing statements (final arguments) are made to jury by the prosecution and the defense . . .
12. The jury deliberates (discusses and decides) and then delivers the verdict. If the jury finds the suspect “GUILTY”. . . The judge is responsible for sentencing.
HOWEVER………
If a suspect is found guilty, the defendant’s lawyer can file a motion for a new trial. The lawyer tells the appellate court why the case should be reviewed. The court can either overturn (reverse) or uphold (keep) the verdict.
2. Authorities place the suspect in a holding cell and make an official record of the arrest-booking.
3. The suspect makes an initial appearance before a magistrate judge who explains the charges makes sure that the suspect is given due process.
4. Next is the preliminary hearing to determine if there is probable cause that the suspect committed the crime.
5. If the case is sent to a grand jury they determine whether an indictment (a formal accusation of a serious crime) will be made.
6. If indicted, the suspect has an arraignment before a superior court. The judge allows the suspect to enter a plea.
7. If a suspect pleads not guilty, a court date is set and a trial is conducted unless a plea bargain is made (suspect admits guilt immediately for a shorter sentence).
8. Trials begin with jury selection.
9. Once the jury is selected, prosecution and defense attorneys present opening statements to the jury.
10 Both sides present evidence and cross-examine witnesses
11. Closing statements (final arguments) are made to jury by the prosecution and the defense . . .
12. The jury deliberates (discusses and decides) and then delivers the verdict. If the jury finds the suspect “GUILTY”. . . The judge is responsible for sentencing.
HOWEVER………
If a suspect is found guilty, the defendant’s lawyer can file a motion for a new trial. The lawyer tells the appellate court why the case should be reviewed. The court can either overturn (reverse) or uphold (keep) the verdict.